- 2021/02/16 - [Go] - Go lang 다운로드 및 설치방법
- 2021/02/17 - [Go] - Golang 시작하기. hello world 찍어보자!
- 2021/02/18 - [Go] - Golang 배우기 실습 : 간단한 모듈 만들어 보기
- 2021/02/18 - [Go] - Golang 배우기 실습 : 내 모듈을 다른 모듈에서 사용해보기
- 2021/02/18 - [Go] - Golang 배우기 실습 : Error(예외) 처리 하기
- 2021/02/22 - [Go] - Golang 배우기 실습 : 한가지 모듈에서 랜덤하게 값 가져오기
여러 사람에 대한 인사말을 받는 기능을 추가해보자.
다중 값을 입력받고 다중 값을 출력하는 로직이다.
여기서 우리는 hello.go를 수정하지 않고, greetings.go 파일에 hellos 메서드를 추가할 것이다.
그런 다음 새 함수가 기존 함수를 호출하도록 로직을 구성해보자.
즉, 원본 로직은 그대로 유지하고 확장된 기능을 구현하는 것이다.
1. greetings/greetings.go 파일을 아래 처럼 수정하자.
- 매개변수가 slice인 Hellos funtion을 추가한다. 또한 반환 유형중 하나를 String 에서 map 으로 변경해서 인사말 메세지에 매핑 된 이름을 반환할 수 있다.
- 새로운 Hellos 함수가 기존의 Hello 함수를 호출 함으로써 두 기능을 모두 유지시킨다.
- message map을 만든다. 각각의 이름과 메세지로 구성되도록 한다. 이때 key 를 이름으로 value를 메세지로 구성한다.
- Go에서는 :make(map[key-type]value-type) 으로 map을 초기화 한다.
- 아래의 for loop에서는 함수가 받은 이름을 반복해서 각각의 값이 비어있지 않은지 확인한 후 다음 메세지를 각각의 value에 연결한다.
- Go 는 따로 인덱스 대신 _ (밑줄)식별자를 사용한다.
package greetings
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
// Hello returns a greeting for the named person.
func Hello(name string) (string, error) {
// If no name was given, return an error with a message.
if name == "" {
return name, errors.New("empty name")
}
// Create a message using a random format.
message := fmt.Sprintf(randomFormat(), name)
return message, nil
}
// Hellos returns a map that associates each of the named people
// with a greeting message.
func Hellos(names []string) (map[string]string, error) {
// A map to associate names with messages.
messages := make(map[string]string)
// Loop through the received slice of names, calling
// the Hello function to get a message for each name.
for _, name := range names {
message, err := Hello(name)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// In the map, associate the retrieved message with
// the name.
messages[name] = message
}
return messages, nil
}
// Init sets initial values for variables used in the function.
func init() {
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
}
// randomFormat returns one of a set of greeting messages. The returned
// message is selected at random.
func randomFormat() string {
// A slice of message formats.
formats := []string{
"Hi, %v. Welcome!",
"Great to see you, %v!",
"Hail, %v! Well met!",
}
// Return one of the message formats selected at random.
return formats[rand.Intn(len(formats))]
}2. hello/hello.go 로 가서 이름으로 그성된 slice를 요청한다. 정상적으로 names/messages의 map이 반환 되는지 확인한다.
아래 처럼 코드를 수정해보자.
- names 라는 slice type의 변수를 생성한다.
- 해당 변수를 이용해 Hellos 메서드를 호출한다.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"example.com/greetings"
)
func main() {
// Set properties of the predefined Logger, including
// the log entry prefix and a flag to disable printing
// the time, source file, and line number.
log.SetPrefix("greetings: ")
log.SetFlags(0)
// A slice of names.
names := []string{"yunji", "jimin", "babo"}
// Request greeting messages for the names.
messages, err := greetings.Hellos(names)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// If no error was returned, print the returned map of
// messages to the console.
fmt.Println(messages)
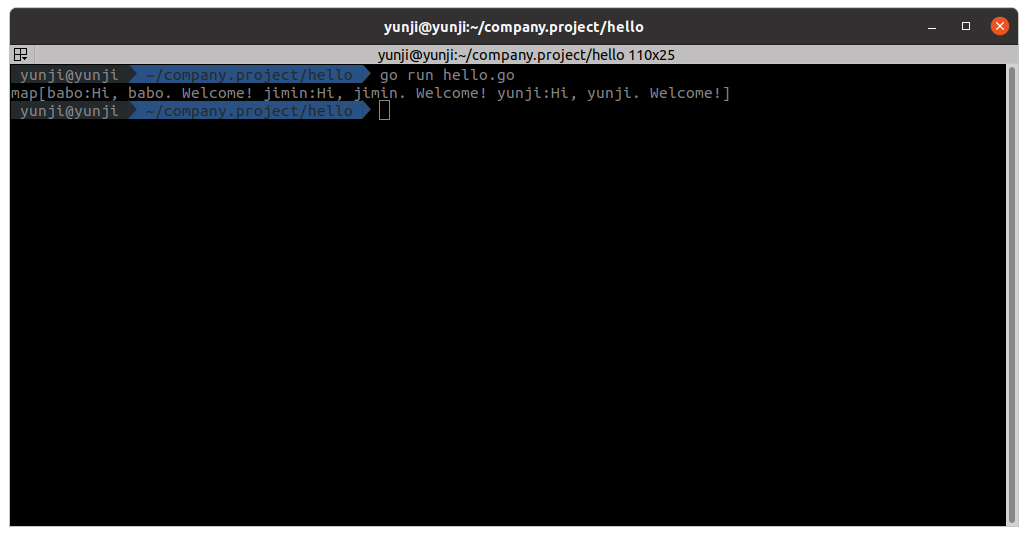
}3. command line으로 와서 hello/hello.go를 실행한다.
아래 처럼 map 형식으로 데이터가 출력되는지 확인한다.
$ go run hello.go
'Backend > Go' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Golang 배우기 실습 : application compile 해서 설치하기 (0) | 2021.02.24 |
|---|---|
| Golang 배우기 실습 : 테스트 코드 추가하기 (0) | 2021.02.23 |
| Golang 배우기 실습 : 한가지 모듈에서 랜덤하게 값 가져오기 (0) | 2021.02.22 |
| Golang 배우기 실습 : Error(예외) 처리 하기 (0) | 2021.02.18 |
| Golang 배우기 실습 : 내 모듈을 다른 모듈에서 사용해보기 (0) | 2021.02.18 |